Hip Pain and Ultrasound-Guided Injections: A Guide to Targeted Relief
Hip pain can be a major obstacle, whether it’s from arthritis, an injury, or overuse, making walking, sitting, or even sleeping uncomfortable. The hip’s complex structure, connecting the pelvis to the leg, is built for stability and mobility, but that also makes it prone to various issues. When rest, physical therapy, or medications aren’t enough, ultrasound-guided injections offer a precise, minimally invasive way to deliver relief directly to the source. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes of hip pain and the different ultrasound-guided injections used to treat it, explained clearly for a general audience.
Understanding Hip Pain
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint where the femur (thigh bone) meets the pelvis, supported by cartilage, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bursae (fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction). Its role in bearing weight and enabling movement makes it susceptible to injury and degeneration. Common causes of hip pain include:
- Osteoarthritis: Cartilage breakdown causing joint pain and stiffness, common in older adults.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of bursae, like the trochanteric bursa on the outer hip, often from repetitive activities.
- Tendinitis or Tendinopathy: Inflammation or degeneration of tendons, such as the gluteal or iliopsoas tendons, from overuse or strain.
- Labral Tears: Damage to the cartilage ring (labrum) around the hip socket, often from trauma or repetitive motions.
- Muscle or Ligament Strains: Injuries to muscles like the hip flexors or ligaments from sports or falls.
- Referred Pain: Pain from the lower back, sacroiliac joint, or even the knee mimicking hip pain.
Symptoms can include aching, sharpness, stiffness, or reduced mobility, often worsening with activity or prolonged sitting. When conservative treatments fall short, ultrasound-guided injections can target the pain source effectively, often delaying or avoiding surgery.Why Ultrasound-Guided Injections?Ultrasound-guided injections use real-time imaging to guide a needle to the precise location needing treatment, such as the hip joint, bursa, or tendon. This approach offers significant advantages over “blind” injections:
- Precision: Ensures medication reaches the exact problem area, critical in the hip’s complex anatomy.
- Safety: Minimizes risk of damaging nerves, blood vessels, or surrounding tissues.
- Effectiveness: Improves outcomes by delivering treatment accurately.
- Comfort: Reduces discomfort with precise needle placement.
Performed by specialists like orthopedists, radiologists, or pain management doctors, these outpatient procedures take 15-30 minutes with minimal recovery time. They’re particularly effective for inflammatory or degenerative hip conditions.
Types of Ultrasound-Guided Injections for Hip Pain
Several ultrasound-guided injections are used to manage hip pain, each tailored to specific conditions. Here’s an overview of the most common options:
1. Corticosteroid Injections
- What They Are: A combination of a corticosteroid (e.g., triamcinolone or methylprednisolone) and a local anesthetic (e.g., lidocaine) to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Target Conditions: Hip osteoarthritis, trochanteric bursitis, or synovitis (inflamed joint lining).
- How They Work: The corticosteroid reduces inflammation in the joint or bursa, while the anesthetic provides immediate pain relief.
- Procedure: Using ultrasound, the doctor injects the mixture into the hip joint (intra-articular) or trochanteric bursa on the outer hip.
- Benefits: Relief can begin within days and last weeks to months. A 2019 study in The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery found that 65-75% of patients with hip osteoarthritis reported significant pain reduction at 12 weeks.
- Considerations: Relief is often temporary, and repeated injections (more than 2-3 per year) may risk cartilage or tendon damage. Not ideal for patients with diabetes due to potential blood sugar increases.
2. Hyaluronic Acid Injections (Viscosupplementation)
- What They Are: Injections of hyaluronic acid, a gel-like substance that mimics the joint’s natural lubricating fluid.
- Target Conditions: Hip osteoarthritis, especially when corticosteroids are ineffective or contraindicated.
- How They Work: Hyaluronic acid cushions the joint, reduces friction, and may support cartilage health, easing pain and improving mobility.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the injection into the hip joint, ensuring accurate delivery to the cartilage.
- Benefits: Can provide relief for 3-12 months. A 2020 review in Clinical Rheumatology reported that 50-60% of hip osteoarthritis patients experienced moderate pain relief and improved function at six months.
- Considerations: May require 1-3 injections over weeks, depending on the formulation. Less effective for severe arthritis, and insurance coverage can be limited. Mild post-injection swelling is possible.
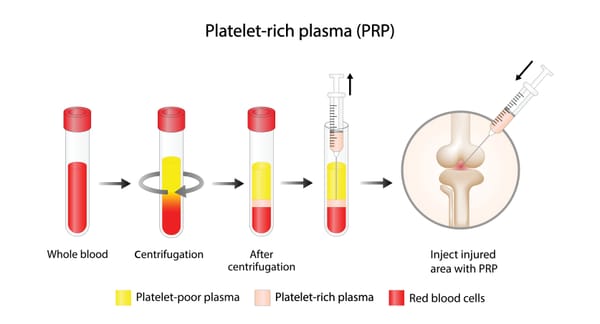
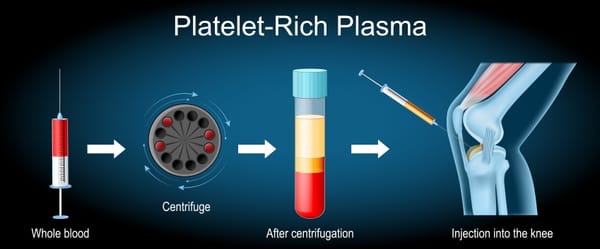
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
- What They Are: A concentrate of platelets from your own blood, rich in growth factors to promote tissue repair.
- Target Conditions: Hip osteoarthritis (mild to moderate), gluteal tendinopathy, or labral tears.
- How They Work: PRP stimulates healing in cartilage, tendons, or the labrum, potentially reducing inflammation and pain.
- Procedure: Blood is drawn, processed to isolate platelets, and injected into the affected area (e.g., hip joint or gluteal tendon) under ultrasound guidance.
- Benefits: May offer longer-term relief (6-12 months) and support tissue regeneration. A 2021 study in American Journal of Sports Medicine found PRP improved pain and function in 60% of hip osteoarthritis patients at one year.
- Considerations: Expensive ($500-$2,000 per injection), often not covered by insurance. Results take weeks and vary by condition severity. More research is needed for consistent protocols.
4. Prolotherapy
- What They Are: Injections of a dextrose (sugar) solution to irritate tissue and stimulate the body’s repair response.
- Target Conditions: Chronic gluteal tendinopathy, ligament laxity, or mild hip osteoarthritis.
- How They Work: The solution triggers mild inflammation, encouraging collagen growth to strengthen tendons or ligaments.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the injection to specific tendons (e.g., gluteus medius) or ligaments around the hip.
- Benefits: May improve stability and reduce pain over months. A 2019 study in Journal of Pain Research reported 50% of patients with chronic hip pain had improved function after 4-6 sessions.
- Considerations: Requires multiple sessions (4-8, spaced weeks apart), and evidence is less robust than for other injections. Temporary soreness post-injection is common.
5. Iliopsoas Bursa or Tendon Injection
- What They Are: Corticosteroid and anesthetic injections targeting the iliopsoas bursa or tendon, located near the front of the hip.
- Target Conditions: Iliopsoas bursitis or tendinitis, often causing groin pain or a “snapping” sensation.
- How They Work: Reduces inflammation in the bursa or tendon, relieving pain and improving hip flexion.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the needle to the iliopsoas bursa or tendon, avoiding nearby structures like the femoral nerve.
- Benefits: Can provide rapid relief, lasting weeks to months. A 2018 study in Skeletal Radiology found 70% of patients with iliopsoas bursitis had significant pain reduction at eight weeks.
- Considerations: Relief may be temporary, and repeated injections carry risks of tendon weakening. Often paired with physical therapy to address underlying causes.
What to Expect from Ultrasound-Guided InjectionsHere’s a general overview of the process:
- Preparation: Your doctor will review your medical history, symptoms, and imaging (e.g., X-ray or MRI) to confirm the diagnosis and choose the appropriate injection. You may need to stop blood thinners or NSAIDs temporarily.
- Procedure: You’ll lie on a table, and the doctor will use ultrasound to visualize the target (e.g., hip joint, bursa, or tendon). After cleaning the skin, they’ll insert a thin needle and inject the medication. Mild discomfort or pressure is normal but brief.
- Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within a day, though strenuous exercise may be limited for 1-2 weeks. Relief timelines vary—corticosteroids act within days, while PRP or prolotherapy takes weeks to months.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include mild soreness, bruising, or swelling at the injection site. Rare risks include infection, nerve injury, or cartilage/tendon damage (with frequent corticosteroids).
Benefits and ConsiderationsBenefits:
- Precise delivery enhances effectiveness and reduces complications.
- Can delay or avoid surgery for conditions like osteoarthritis or bursitis.
- Supports rehabilitation by reducing pain, enabling better participation in physical therapy.
- Minimally invasive with quick recovery.
Considerations:
- Effectiveness depends on the condition, injection type, and patient factors (e.g., age or disease severity).
- PRP and hyaluronic acid injections are costly and often not covered by insurance.
- Relief may be temporary, requiring repeat injections or complementary treatments.
- Severe cases (e.g., advanced arthritis or large labral tears) may still require surgery.
Are Ultrasound-Guided Injections Right for You?
Ultrasound-guided injections are typically considered when conservative treatments (rest, physical therapy, or oral medications) fail to provide adequate relief, but before surgical options like hip replacement or arthroscopy.
They’re ideal for inflammatory or degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis, bursitis, or tendinopathy. Your doctor will evaluate:
- The cause and severity of your hip pain, using exams and imaging.
- Your overall health (e.g., diabetes or bleeding disorders may limit options).
- Your goals, such as pain reduction, improved mobility, or delaying surgery.
Before proceeding, discuss the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes with your provider. Choosing a specialist experienced in ultrasound-guided hip injections is critical, as the hip’s deep anatomy requires precision.
Looking Ahead
Ultrasound-guided injections are a powerful tool for managing hip pain, offering targeted relief with minimal downtime. While not a cure, they can significantly improve quality of life and complement treatments like physical therapy or bracing. Ongoing research, including trials listed on Clinicaltrials.gov, continues to refine these approaches, with PRP and regenerative therapies showing growing potential for long-term benefits.
If hip pain is limiting your daily life, talk to an orthopedist, rheumatologist, or pain specialist about whether ultrasound-guided injections could help. Online communities, like those on Reddit or through the Arthritis Foundation, can provide support and insights from others with similar experiences.
Hip pain doesn’t have to keep you on the sidelines. With options like ultrasound-guided injections, relief is within reach—take the first step and explore your path to a more comfortable life.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider before considering ultrasound-guided injections or any new treatment for hip pain.