Shoulder Pain and Ultrasound-Guided Injections: A Guide to Relief
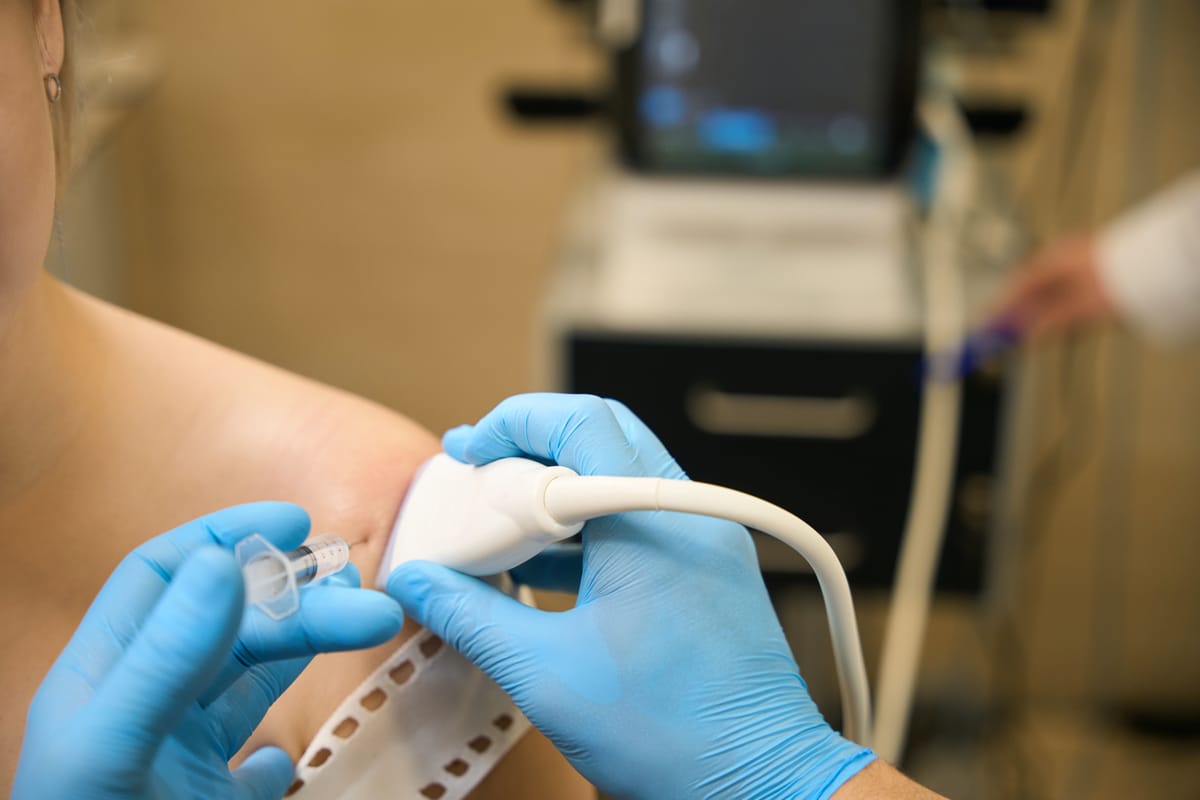
Shoulder pain can be a real roadblock, whether it’s from an injury, overuse, or a chronic condition. It can make simple tasks like reaching for a shelf or throwing a ball feel daunting. While rest, physical therapy, or medications often help, some people need more targeted solutions. That’s where ultrasound-guided injections come in—a precise, minimally invasive way to deliver relief right where it’s needed. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes of shoulder pain and the different ultrasound-guided injections used to treat it, explained clearly for everyone.
Understanding Shoulder Pain
The shoulder is a complex joint, relying on muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones (like the humerus, scapula, and clavicle) to move smoothly. Its flexibility makes it prone to injury and wear. Common causes of shoulder pain include:
- Rotator Cuff Issues: Tears, tendinitis, or impingement in the group of muscles and tendons stabilizing the shoulder.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction in the joint.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis causing joint inflammation and cartilage breakdown.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): Stiffness and pain from a tightened joint capsule.
- Labral Tears: Damage to the cartilage ring around the shoulder socket.
- Tendon or Ligament Strains: Overuse or trauma, like in sports or heavy lifting.
Symptoms can range from dull aches to sharp pain, stiffness, or weakness, often worsening with movement. When conservative treatments like rest, ice, or physical therapy aren’t enough, ultrasound-guided injections offer a precise way to manage pain and promote healing.
Why Ultrasound-Guided Injections?
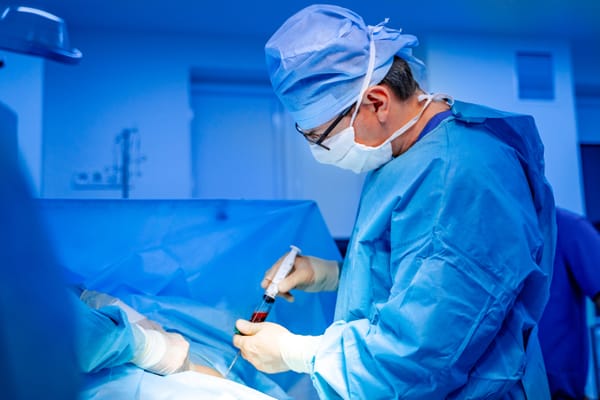
Ultrasound-guided injections use real-time imaging to guide a needle to the exact spot needing treatment, improving accuracy and effectiveness compared to “blind” injections. Benefits include:
- Precision: Targets specific structures like tendons, joints, or bursae.
- Safety: Reduces risk of hitting nerves or blood vessels.
- Comfort: Minimizes discomfort by ensuring correct needle placement.
- Outpatient Procedure: Quick, often done in 15-30 minutes, with minimal recovery time.
These injections are performed by specialists like radiologists, pain management doctors, or orthopedists, typically in a clinic or hospital setting.
Types of Ultrasound-Guided Injections for Shoulder Pain
Several ultrasound-guided injections are used to treat shoulder pain, each tailored to the underlying issue. Here’s a look at the most common options:1. Corticosteroid Injections
- What They Are: A combination of a corticosteroid (like triamcinolone or methylprednisolone) and a local anesthetic (like lidocaine) to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Target Conditions: Rotator cuff tendinitis, subacromial bursitis, shoulder arthritis, or adhesive capsulitis.
- How They Work: The corticosteroid reduces inflammation in the joint, tendon, or bursa, while the anesthetic provides immediate pain relief.
- Procedure: Using ultrasound, the doctor injects the mixture into the affected area, such as the subacromial space or glenohumeral joint.
- Benefits: Relief can start within days and last weeks to months. A 2019 study in The American Journal of Sports Medicine found that ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injections for subacromial pain improved pain scores by 50% in 70% of patients at six weeks.
- Considerations: Relief may be temporary, and repeated injections (more than 2-3 per year) can weaken tendons or cartilage. Not ideal for all patients, like those with diabetes, due to possible blood sugar spikes.
2. Hyaluronic Acid Injections
- What They Are: Injections of hyaluronic acid, a gel-like substance that mimics the joint’s natural lubricating fluid.
- Target Conditions: Shoulder osteoarthritis, especially when corticosteroids aren’t suitable.
- How They Work: Hyaluronic acid cushions the joint, reduces friction, and may promote cartilage health.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the injection into the glenohumeral joint, ensuring the fluid reaches the cartilage.
- Benefits: Can improve joint mobility and reduce pain for 3-6 months. A 2021 review in Clinical Rheumatology noted moderate pain relief in osteoarthritis patients, though results vary.
- Considerations: Less effective for severe arthritis. Multiple injections (1-5 weekly) may be needed, and insurance coverage can be limited.
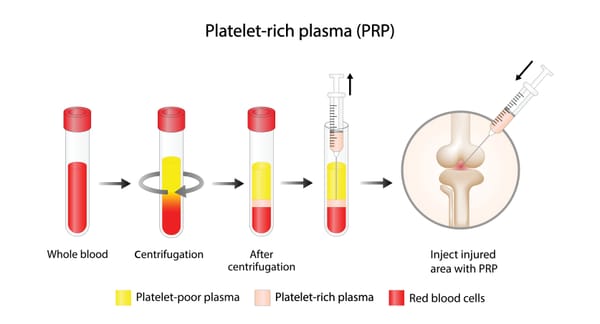
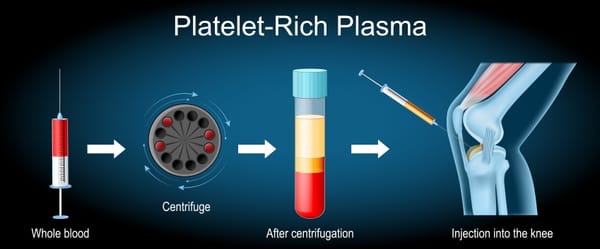
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
- What They Are: A concentration of platelets from your own blood, rich in growth factors that promote tissue repair.
- Target Conditions: Rotator cuff tears (partial), tendinopathy, or mild osteoarthritis.
- How They Work: PRP stimulates healing in damaged tendons or cartilage, potentially reducing inflammation and pain.
- Procedure: Blood is drawn, processed to isolate platelets, and injected into the affected area (e.g., rotator cuff tendon) under ultrasound guidance.
- Benefits: May support long-term healing, especially for chronic injuries. A 2022 study in Orthopedic Journal of Sports Medicine found PRP improved function in 60% of patients with partial rotator cuff tears after six months.
- Considerations: Expensive, often not covered by insurance. Results take weeks and vary based on injury severity. More research is needed for consistent outcomes.
4. Prolotherapy
- What They Are: Injections of a dextrose (sugar) solution to irritate tissue and stimulate repair.
- Target Conditions: Chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy or ligament laxity causing instability.
- How They Work: The solution triggers a mild inflammatory response, encouraging the body to strengthen tendons or ligaments.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the injection to specific tendons or ligaments around the shoulder.
- Benefits: May improve stability and reduce pain over time. Small studies, like one in Pain Physician (2020), suggest modest improvements in chronic shoulder pain.
- Considerations: Requires multiple sessions (4-6) and takes weeks to months for results. Evidence is limited, and it’s less commonly used than other injections.
5. Nerve Blocks (Suprascapular Nerve Block)
- What They Are: Anesthetic (sometimes with a steroid) injected near the suprascapular nerve, which supplies the shoulder.
- Target Conditions: Frozen shoulder, severe arthritis, or post-surgical pain when other injections aren’t feasible.
- How They Work: Blocks pain signals from the shoulder, providing temporary relief and aiding physical therapy.
- Procedure: Ultrasound guides the needle to the suprascapular notch, where the nerve is located.
- Benefits: Can provide immediate pain relief, lasting days to weeks. A 2018 study in Pain Medicine found suprascapular nerve blocks improved pain and range of motion in 65% of frozen shoulder patients.
- Considerations: Relief is temporary, and repeated blocks may be needed. Risks include nerve irritation, though rare with ultrasound guidance.
What to Expect from Ultrasound-Guided Injections
Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Preparation: Your doctor will review your medical history and imaging (e.g., MRI) to confirm the diagnosis and choose the right injection. You may need to stop blood thinners temporarily.
- Procedure: You’ll sit or lie down, and the doctor will use ultrasound to locate the target area. After cleaning the skin, they’ll insert a thin needle and inject the medication. Mild discomfort is normal but brief.
- Recovery: Most people resume normal activities within a day, though strenuous exercise may be limited for 1-2 weeks. Pain relief varies—corticosteroids act quickly, while PRP or prolotherapy takes weeks.
- Side Effects: Mild soreness, bruising, or swelling at the injection site is common. Rare risks include infection, nerve injury, or tendon weakening (with corticosteroids).
Benefits and Considerations
Benefits:
- Precise delivery improves effectiveness and reduces complications.
- Can delay or avoid surgery for conditions like rotator cuff tears or arthritis.
- Often complements physical therapy by reducing pain enough to improve movement.
Considerations:
- Results vary based on the condition, injection type, and patient factors (e.g., age or injury severity).
- Some injections (PRP, hyaluronic acid) are costly and may not be covered by insurance.
- Temporary relief may require repeat injections or additional treatments.
- Not all patients respond, and severe cases (e.g., full rotator cuff tears) may need surgery.
Are Ultrasound-Guided Injections Right for You?
Ultrasound-guided injections are typically considered when conservative treatments (rest, physical therapy, or oral medications) fail, but before surgery. They’re best for inflammatory or degenerative conditions like tendinitis, bursitis, or mild arthritis. Your doctor will assess:
- The cause and severity of your shoulder pain (via exam and imaging).
- Your overall health (e.g., diabetes or bleeding disorders may affect options).
- Your goals, whether reducing pain, improving function, or delaying surgery.
Before proceeding, discuss the injection’s risks, benefits, and expected outcomes with your doctor. Finding a provider experienced in ultrasound-guided techniques is crucial for optimal results.
Looking Ahead
Ultrasound-guided injections are a powerful tool for managing shoulder pain, offering targeted relief with minimal downtime. While they’re not a cure, they can significantly improve quality of life and support other treatments like physical therapy. Ongoing research, including trials on Clinicaltrials.gov, continues to refine these techniques, with PRP and regenerative therapies showing particular promise.
If shoulder pain is holding you back, talk to an orthopedist or pain specialist about whether ultrasound-guided injections could help. Communities like those on Reddit or patient advocacy groups (e.g., Arthritis Foundation) can also provide support and shared experiences.
Shoulder pain doesn’t have to define your days. With options like ultrasound-guided injections, relief may be closer than you think—keep exploring and advocating for your health.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider before considering ultrasound-guided injections or any new treatment for shoulder pain.